Chapter 16
Light
Here is the answer of chapter 16 LIGHT of NCERT science of class 8.The complete solution of CHAPTER 16 LIGHT is given here which is prepared subject expert. Some important extra questions and important points about Chapter 16 are also given.
Ques1:-Suppose you are in a dark room can you see object in the room? Can you see object outside the room.Explain.
Ans 1. When we are in a dark room, we cannot see the object in the room because there is no light being reflected by the object.However, we can see the object outside the room because they reflect light falling on them.
Ques2:-Differentiate between regular and diffused reflection does diffused reflection mean the failure of the law of reflection.
Ans 2.In regular reflection, all the rays that are reflected from the surface are parallel to each other. In diffused reflection the reflected light consists of rays that are not parallel to each other. Diffused reflection does not mean the failure of the law of reflection. Diffused reflection occurs when the surface is rough.
On a rough surface the angle of incidence change from one ray to the other.
Ques 3. Mention against each of the following whether regular or diffused reflection will take place when a beam of light strikes.Justify your answer in each case.
a)Polish wooden table.
b)Chalk Powder
c) Cardboard Surface
d) Marble floor with water spread over it
e)Mirror
f)Piece of Paper
Ans.a) The wooden table that has been a polished regular reflection. The surface that have been recently polished can be a Good example of a smooth surface. The wooden table that has been polished has a smooth surface.
b) White Chalk Powder that is used in school - Diffused reflection.
Chalk Powder spread on surface is an example of irregular surface. Hence,it is rough.Therfore,the diffused reflection will appear from chalk Powder.
c) Cardboard Surface- Diffused Reflection
The surface of the Cardboard is a kind of irregular surface. Hence, the diffused reflection will take place from a cardboard surface.
d) Marble floor- Regular reflection
Marble floor can be a good example of a surface that is regular. Because water make the creamic glossy. Thus, the reflection that are regular occur on this surface.
e) Mirror- Regular Reflection
A mirror has a very smooth surface hence it gives a regular reflection.
f)Piece of Paper- Diffused Reflection
Although a piece of paper may look smooth,it has many irregularities on its surface. Because of this reason,it will give you a diffused reflection.
Ques 4. State the Law of Reflection.
Ans. The law of reflection states that:-
a) The angle of incidence and angle of reflection both are always equal to one another.
b) The reflected ray, the incident ray, the ray normal to the reflective surface at the point of incidence all come on the same plane.
Ques 5. Describe an activity to show that the incident ray,the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
Ans.On a table,place a plane Mirror perpendicular to the plane of the table.Make a small hole in a paper and hold it perpendicular to the plane of the table. Try to do this experiment in a dark room. Make one more piece of paper which is on the table. Now beam light rays with the help of torch through the small hole such that the beam of light hits the normal at the bottom of the mirror. The ray of light will be reflected in a light rays from the hole are incident on the mirror.Looking at the piece of paper on the table, we can easily show that the incident ray,the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
Ques 6. Fill in the blanks in the following:-
a) A person 1m in front of a plane Mirror seems to be_______m away from his image.
b) If you touch your _______ ear with right hand in front of plane mirror it will be seen in the mirror that your right ear is touched with _________.
c)The size of the pupil becomes_________ when you see in dim light.
d) Night birds have__________ cones than rods in their eyes.
Ans. a) 2
b) Left, Left hand
c) Large
d) Fewer
Choose the correct option in Questions 7-8
Ques 7. Angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
a) Always
b) Sometimes
c) Under special conditions
d) Never
Ans 7. Always.
Ques 8. Image formed by a plane mirror is
a) virtual,behind the mirror and enlarged.
b) virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
c) real at the surface of the mirror and enlarged.
d) real, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
Ans 8. Virtual,behind the mirror and enlarged.
Ques 9. Describe the construction of Kaleidoscope.
Ans. Three rectangular mirror strips are joined together to form a prism as shown in the figure. This prism is placed inside a circular wooden tube whose length is slightly longer than the length is the prism. One end of the tube is closed with a cardboard disc with a hole at the centre,and at the other end is closed with a plane glass plate. On this glass plate, several small piece of colured bangles are placed. This end is closed by a round glass plate,so that there is sufficient space for the bangle pieces to move.
Ques 10. Draw a labelled sketch of the Human eye.
Ques 11. Gurmit wanted to perform activity 16.8 using a laser torch. Her teacher advised her not to do so. Can you explain the basis of the teacher's advise?
Ans. The laser beam produced by a laser torch has high energy that can damage the retina of the eye. Hence, the teacher advised Gurmit not to use laser torch.
Ques 12. Explain how you can take care of your eyes.
Ans. a) Get your eyes checked regularly by an eye specialist.
b) Do not look at sun on bright light directly.
c) Do not read in insufficient light.
d) When foreign particles enter your eyes,do not rub them; instead wash them with clean water.
e)While watching TV, do not sit very close to it.
Ques 13. What is the angle of incidence of a ray if the reflected ray is at an angle of 90° to the incident ray?
Ans. The angle between an incident ray and its reflected ray is twice the angle of incidence. Hence, in this case,the angle of incidence is 45°.
Ques 14. How many image of a candle will be formed if it is placed between two parallel plane mirror seperate by 40cm?
Ans. An infinite number of images of a candle will be formed if it is placed between two parallel plane mirror. The number of image formed does not depend on the distance between the mirror.
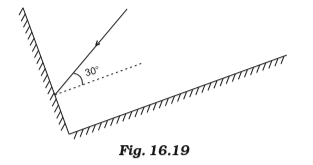
Ques15 .Two mirrors meet at right angles.A ray of light is incident on one at an angle of 30 as shown in the figure.Draw the reflected ray from the second mirror.
Ans. The first law of reflection is used to obtain the path of reflected light.
It can be observed that the given ray of light will reflect from the second mirror at an angle of 60°.
Ques16 Bhoojo stand at A just on the side of the plane mirror as shown in Fig.16.20. can he see himself in the mirror? also can he see the image of objects situated at P,Q and R.
Ans 16.Bhoojo cannot see himself in the mirror he can see the images of the object situated at P and Q, but cannot see the image of R.
Ques17 A)Find out the position of the image of an object situated at A in the plane mirror.
B)Can paheli at B see this image?
C)Can bhoojo at C see this image?
D)When paheli moves from B to C, where does the image of A move?
Ans17 A)The image of A is formed behind the mirror at the same distance as A is in the front of the mirror.
B)Paheli at B can see the image of A.
C)Boojho at C can see the image of A.
D)When paheli moves from B to C,the image of A does not move.
This is the complete solution of CHAPTER 16 LIGHT. This is according to latest syllabus of CBSE 2020-21.
Here's some important points about the CHAPTER 16 LIGHT of class 8 Science NCERT.
Define the terms:-
1)Luminous bodies- The bodies which emits light on thier own are called luminous bodies.The sun, stars, burning candle, filament of electric bulb etc are called luminous bodies.
2)Non luminous bodies-The bodies which do not emit light on thier own but reflects the light falling on them are called non-luminous bodies. Forex:-moon.
3)Opaque-A body which obserbs some of light falling on it and reflects the remaining are called opaque.
4)Transparent body-A body which permits maximum amount of light to pass through them and reflects very little amount of them.
5)Translucent body-A body which partially allow the light to penetrate it and reflects the remaining light.
6)Eye lens-The eye lens is a convex lens made up of transparent jelly like material,the eye lens is held in position by cilliary muscles.
7)Cornea-It is transparent spherical membrane infront of the eye,light enters eye through cornea.
8)Spectrum-The spliting of white lights into seven colours is called spectrum of light.
These are some important points of Chap 16.
Here's is some extra Questions about the Chapter 16 LIGHT of NCERT SCIENCE CLASS 8.
Extra ques/answers
Ques 1 Why is the moon not considered as luminous bodies?
Ans1 The moon is not considered as luminous body, because it does not emit its own light, it reflects the light of the sun.
Ques2 Write three uses of plane mirror?
Ans2] 1)As a looking mirror.
2)As a reflector in solar cookers.
3)For signaling by army personnel.
Ques3 Write three characteristics of image formed by plane mirror.
Ans3]1) Image is virtual it means it cannot be seen on screen.
2) Image is erect and is of the same same size as that of the object.
3)Image is formed as far behind the mirror as the object is.



Comments
Post a Comment
Don't worry,We don't spam.