Chapter 6
Tissue
Here is the answer of chapter 6 Tissue of NCERT science of class 9.The complete solution of CHAPTER 6 Tissue is given here which is prepared subject expert.
Block Questions Page No- 69
Ques 1. What is tissue?
Ans. Tissue is a group of cells that are similar in structure and are organised together to perform specific task.
Ques 2. What is the utility of tissue in multicellular organisms?
Ans. In unicellular organisms, a single cell performs all the basic function such as respiration,movement, excretion, digestion,etc. But in multicellular organisms, cells are grouped to form tissues. This tissues are specialized to carry out a particular function at a place in the body. For example: the muscle cell form muscular tissue which help in movement, nerve cells form the nervous tissue which helps in transmission of message. This is known as division of labour that multicellular organisms. It is because of my division of labour that multicellular organisms are able or perform all functions efficiently.
Page no- 73
Ques 1. Name types of simple tissue.
Ans. Simple Permanent tissues are of three types. Parenchyma, schlerenchyma and collemchyma. Parenchyma Tissue is of further two types- aerenchyma and chlorenchyma.
Ques 2. Where is apical meristem found?
Ans. Apical meristem is present at the growing tips of stem and roots. Their main function is to initiate growth in new cells of seedlings at the tips of roots and shoots.
Ques 3. Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Ans. The husk of coconut is made up of Sclerenchyma.
Ques 4. What are the constitute of phloem?
Ans. Phloem is the food conducting tissue in plant. It is made up of four components.
I)Sieve tubes
II) Companion cells
III)Phloem parenchyma
IV) Phloem fibres
Page No 78
Ques 1. Name the tissue responsible for the movement of our body.
Ans. The muscular tissue is responsible for the movement of our body.
Ques 2. What does a neuron looks like?
Ans. A neuron consist of a cell body with a nucleus and cytoplasm. It has two important extensions known the axon and dendrites. An area is a long thread like extension of nerve cell that transmits impulses. Thus, the neuron transmits impulses away from the cell body. Whereas the dentrites recieve nerve impulses. This coordinated functions help in transmitting impulses very quickly.
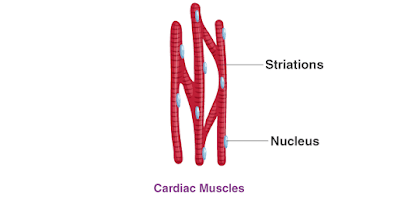
Ques 3. Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Ans Three features a cardiac muscles are:-
I) cardiac muscles are involuntary muscles that contract rapidly but do not yet fatigued.
II) They control the contraction and relaxation of the heart.
III) The cell of cardiac muscles are cylindrical, branched and uninucleated.
Ques 4. What are the function of areolar tissue?
Ans. Function of areolar tissue:-
I) it helps in supporting internal organ.
II) it helps in repairing the tissue of skin and muscles
Exercise
Ques 1. Define the term 'Tissue'.
Ans. The group of cells similar in structure that work together to achieve a particular function form of tissue. This group of cell has a common origin.
Ques 2. How many type of element together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Ans. xylem is a complex tissue. It is made up of following four kind of cells or elements
a) tracheids
b) vessels
c) xylem parenchyma
d) xylem fibres
Ques 3. How are simple tissues different from complex tissue in plants?
Ans. Simple tissues are made up of one type of cell which coordinate to perform a common function complex tissues are made up of more than one type of cell. All these coordinate to perform a common function.
Ques 4. Difference between parenchyma, collenchyma and Sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall.
Ans.
The following are the differences based on cell wall between different tissues:
| Parenchyma | Collenchyma | Sclerenchyma |
| Cell walls are thin and made up of cellulose | Cell walls are thick at the edges due to the deposition of pectin | Cell walls are thick due to the deposition of lignin |
Ques 5. What are the functions of stomata?
Ans. The small pores present in the epidermis of the leaf are stomata. Stomata are enclosed by two kidney shaped cell called guard cell.
Function of stomata:-
•exchange of gases,particularly CO2 and O2 with atmosphere.
•Loss of water in the form of vapour during evaporation.
Ques 6. Diagrammatically show the difference between three types of muscles fibres.
Ans. There are three types of Muscles Fibre. they are as follows;
1.Cardiac Muscles
a) It is present in heart.
b)It is involuntary in nature.
c)The muscles fibres are branched.
2.Smooth Muscles
a)It is found in lungs and alimentary canal.
b)It is involuntary in nature.
c)It has 1 nuclei.
d)it is spindle shaped.
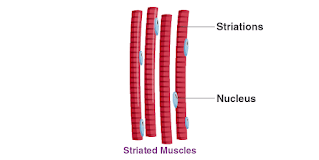
3.Striated Muscles
a)It is connected with bones.
b)It is voluntary in nature.
c)It poses many nuclei.
d)Striated muscles are branched.
Ques 7. What is the specific function of Cardiac Muscles?
Ans. Cardiac muscles are involuntary muscles which show characteristics of both smooth and striated muscles. These muscles occur in the wall of heart.
Functions of Cardiac Muscles:-
• Cardiac muscles contract and relax rapidly, rhythmically, and tirelessly throughout life.
•The contraction and relaxation of heart muscles help to pump and distribute blood to various part of the body..
Ques 8. Difference between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
Ans.The following are the differences between different types of muscles based on their structure and location in the body.
| Character | Striated muscles | Un-striated muscles | Cardiac muscles |
| Shape/Structure | Long, cylindrical, non – tapering. They are un-branched. | Long and tapering. They are un – branched. | Cylindrical and non – tapering. They are branched. |
| Location in body | Hands, legs and skeletal muscles | Wall of stomach, intestine, ureter and bronchi | Heart |
| Dark and light bands | Present | Absent | Present but less prominent |
Ques 9. Draw a labelled diagram of Neuron.
Ques 10. Name the following:-
a) Tissue that form inner lining of our mouth.
b) Tissue that connects muscles to bones in humans.
c) Tissue that transfer food in plants.
d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
e) Connective tissue with fluid matrix.
f)Tissue present in brain.
Ans.a) Squamous epithelium
b) Tendon
c) phloem
d) Adipose tissue
e) Blood
f) Nervous tissue
Ques 11. Identify the types of tissues in the following:
Skin, bark of tree , bone , lining of kidney tubule , vascular bundle.
Ans. Skin- stratified squamous epithelium
Bark of tree- cork protective tissue
Bone - connective tissue
Lining of kidney tubule - Cuboidal epithelium ( Cuboidal epithelium tissue)
Vascular Bundle- complex permanent tissue (phloem and xylem)
Ques 12. Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Ans. Parenchyma is simple permanent tissue of angiospermic plants. It is present in cortex and pith of stem and roots, it is also present in mesophyll of leaves when it contains chlorophyll. It is called chlorenchyma found in green leaves.
Ques 13. What is the role of epidermis plants?
Ans. Epidermis is a protective tissue of angiospermic plants. It provide protection to underlying tissue. Epidermis forms outer covering of various plants organ such as roots, stems, leaves and flowers and remains in direct contact with the environment. Any substance wheater solid, liquid and gas can enter into plants or move outside only after passing through this layer. Epidermis helps in absorption, secretion , gaseous exchange and transpiration. It helps in preventing the entry of pathogens.
Ques 14. How does a cork act as a protective tissue?
Ans. The cork cells are dead cell and do not have any intercellular space. The cell wall of the cork slice are coated with suberin (a waxy substance)
suberin make these cell impermeable to water and gases cork is protective in function. It protects underlying tissue from infection and mechanical injury.
Ques 15. Complete the following chart.
These are the complete notes of CHAPTER 13 WHY DO WE FALL ILL OF SCIENCE NCERT CLASS 9. Hope these notes helpful to better understand the CHAPTER 6 TISSUE.
FOR ANY PLEASE CONTACT US-
We are here to solve your queries-
Related links





Comments
Post a Comment
Don't worry,We don't spam.